Nziakou Y., George M., Fisher G., Bresson B., Roux S., Halary J.L. and Ciccotti M., 2022. Bridging steady-state and stick-slip fracture propagation in glassy polymers. Soft Matter, 18, 793-806.
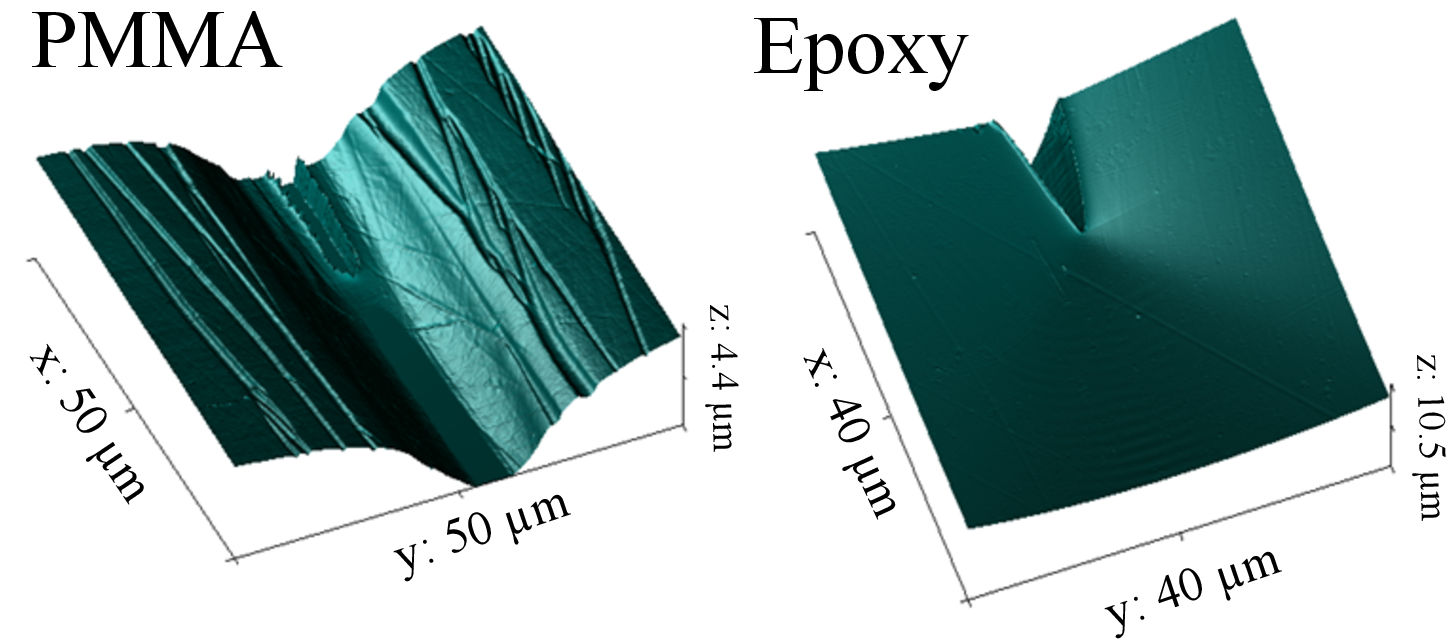
Both an experimental and a theoretical investigation of fracture propagation mechanisms acting at the process zone scale in glassy polymers are presented. The main aim is to establish a common modeling for different kinds of glassy polymers presenting either steady-state fracture propagation or stick-slip fracture propagation or both, depending on loading conditions and sample shapes. From the experimental point of view, new insights are provided by the in situ AFM measurements of viscoplastic strain fields acting within the micrometric process zone in a brittle epoxy resin, which highlight an extremely slow unexpected steady-state regime with finite plastic strains of about 30% around a blunt crack tip, accompanied by propagating shear lips. From the theoretical point of view, we apply to glassy polymers some recently developed models for describing soft dissipative fracture that are pertinent with the observed finite strains. We propose a unified modeling of fracture energy for both the steady-state and stick-slip fracture propagation based on the evaluation of energy dissipation density at a characteristic strain rate induced in the process zone by a competition between the crack propagation velocity and the macroscopic sample loading rate.


