Fourton P., Piroird K., Ciccotti M and Barthel E., 2020.
Adhesion rupture in laminated glass : influence of adhesion on the energy dissipation mechanisms. Glass Struct Eng. 5, 397–410. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40940-020-00136-4.
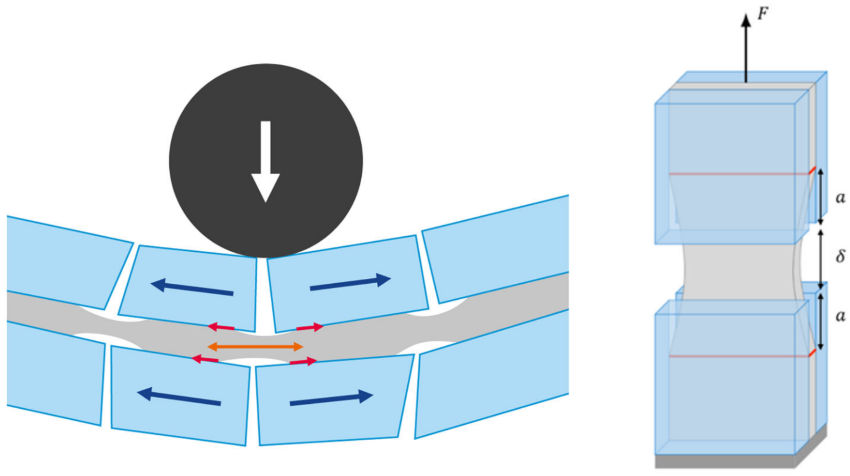
When laminated glass shatters underimpact, most of the energy dissipation occurs in thecoupled delamination and stretching of the polymerinterlayer between broken chunks of glass. The strongdependency of these mechanisms on interlayer nature,on loading rate and on temperature has been previ-ously investigated : however, the effect of the interfa-cial adhesion is unexplored. In this work, a surfacemodification technique is proposed, along with amechanical characterization of the debonding with theThrough Crack Tensile Test. We show that whileincreasing adhesion has the effect of enhancing theenergy required to propagate the delamination frontsas well as the stretch level of the delaminatedinterlayer, the diss ipation associated to the stretchingof the volume of the PVB interlayer seems unaffected.We attribute this effect to the competition between thechanges in both stretch and stretch rate in theviscoelastic interlayer. Finally, we discuss the exper-imental observation of the limits of the steady-statedebonding regime, related to the competition betweenadhesive crack propagation and cohesive failure in theinterlayer.


